
 Holidaypac
Holidaypac
 Oct 22,2024
Oct 22,2024

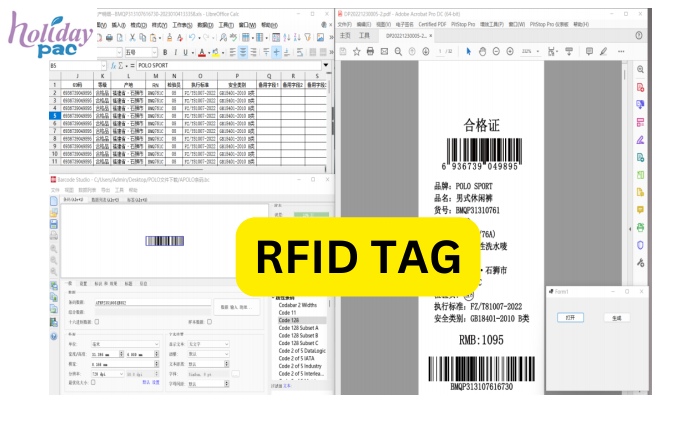
RFID technology operates by enabling a reader to communicate with a tag using radio waves. The tag, which contains an integrated circuit and an antenna, transmits data back to the reader when activated. This communication can occur without requiring a direct line of sight, unlike traditional barcode systems, making RFID particularly advantageous for various applications
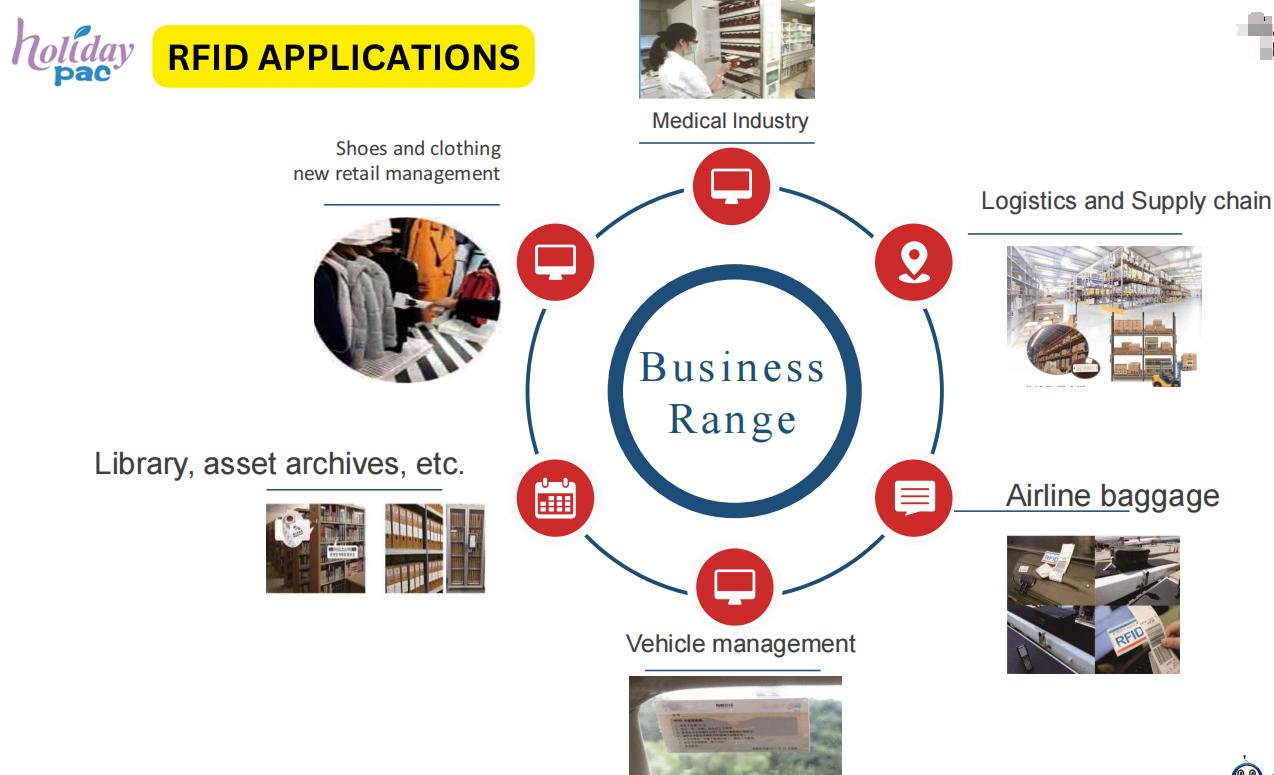
RFID technology is employed across multiple industries for various purposes, including:
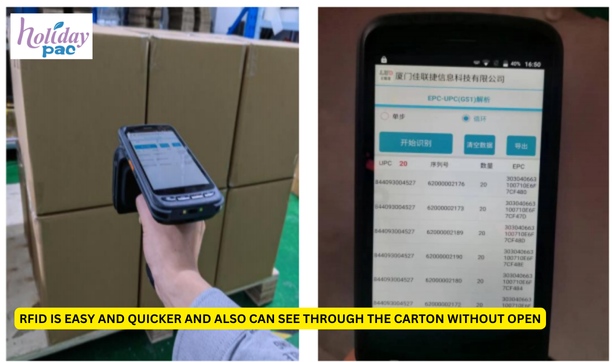
RFID offers several key advantages over traditional barcode systems:
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and barcode technologies are both widely used for tracking and identifying items, but they differ significantly in functionality, efficiency, and application. Here’s a comparison based on key factors:
|
Feature |
RFID |
Barcode |
|
Technology |
Uses radio waves to communicate between tags and readers. |
Relies on optical scanning of printed patterns. |
|
Data Storage |
Can store larger amounts of data, including unique identifiers and additional information. |
Limited data storage, typically just a product ID. |
|
Readability |
Can be read without line-of-sight and can scan multiple tags simultaneously. |
Requires direct line-of-sight for scanning each item individually. |
|
Range |
Can read tags from several feet away, depending on the type of tag and reader. |
Typically requires close proximity to the scanner. |
|
Durability |
More durable and resistant to damage from environmental factors (e.g., moisture, dirt). |
Susceptible to wear and tear; can become unreadable over time. |
|
Cost |
Generally higher initial costs due to the price of tags and readers. |
More cost-effective and easier to implement in many scenarios. |

Contact with us by info@holidaypac.com or whatisapp+86 18124670856

Links